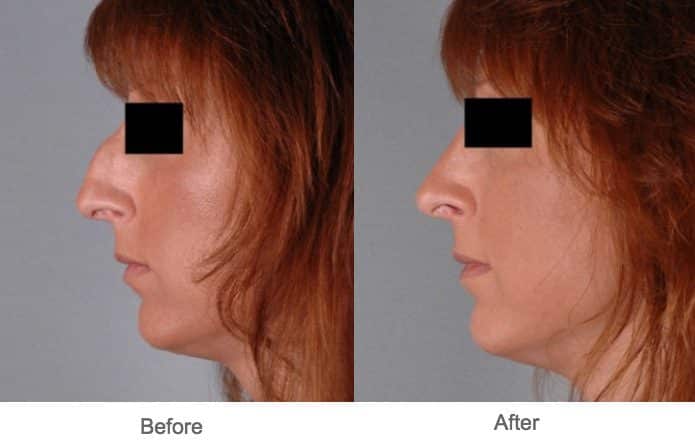
Rhinoplasty Austin Tx Fundamentals Explained
Table of ContentsHow Rhinoplasty Surgery Austin can Save You Time, Stress, and Money.Some Of Nose Job Austin TxGet This Report about Nose Job
Lower third area the skin of the lower nose is as thicker and less mobile, since it has more sebaceous glands, specifically at the nasal tip. Subcutaneous fat layer is very thin. Nasal lining At the vestibule, the human nose is lined with a mucous membrane of squamous epithelium, which tissue then transitions to become columnar respiratory epithelium, a pseudo-stratified, ciliated (lash-like) tissue with plentiful seromucous glands, which maintains the nasal wetness and safeguards the respiratory tract from bacteriologic infection and foreign things.
the elevator muscle group that includes the procerus muscle and the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle. the depressor muscle group that includes the alar nasalis muscle and the depressor septi nasi muscle. the compressor muscle group which consists of the transverse nasalis muscle. the dilator muscle group which consists of the dilator naris muscle that expands the nostrils; it remains in 2 parts: (i) the dilator nasi anterior muscle, and (ii) the dilator nasi posterior muscle.
To prepare, map, and execute the surgical correction of a nasal problem or deformity, the structure of the external nose is divided into nine (9) visual nasal subunits, and six (6) visual nasal segments, which supply the plastic cosmetic surgeon with the measures for identifying the size, extent, and topographic area of the nasal flaw or defect.
For this reason, if more than 50 percent of a visual subunit is lost (harmed, malfunctioning, damaged) the surgeon replaces the whole visual sector, normally with a local tissue graft, harvested from either the face or the head, or with a tissue graft harvested from elsewhere on the client's body. Like the face, the human nose is well vascularized with arteries and veins, and therefore provided with abundant blood.
The external nose is provided with blood by the facial artery, which becomes the angular artery that courses over the superomedial element of the nose. The sellar region (sella turcica, "Turkish chair") and the dorsal area of the nose are supplied with blood by branches of the internal maxillary artery (infraorbital artery) and the ophthalmic arteries that originate from the internal typical carotid artery system.
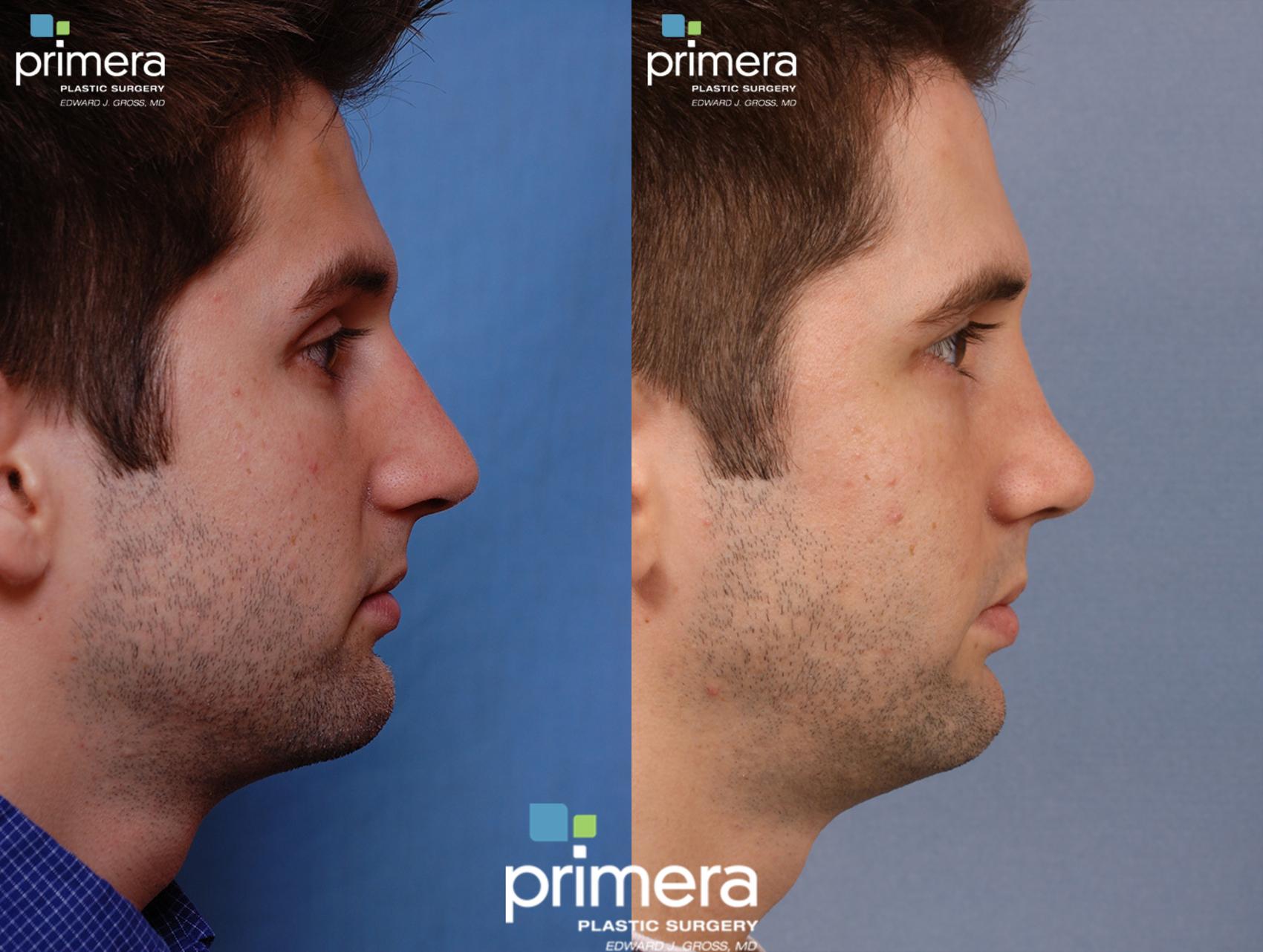
The Best Strategy To Use For Rhinoplasty Austin Tx
The nasal septum also is provided with blood by the sphenopalatine artery, and by the anterior and posterior ethmoid arteries, with the additional circulatory contributions of the remarkable labial artery and of the higher palatine artery - rhinoplasty austin. These 3 (3) vascular products to the internal nose converge in the Kiesselbach plexus (the Little location), which is an area in the anteroinferior-third of the nasal septum, (in front and below).
The nasal veins are biologically substantial, since they have no vessel-valves, and since of their direct, circulatory interaction to the spacious sinus, which makes possible the possible intracranial dispersing of a bacterial infection of the nose. For this reason, because of such a plentiful nasal blood supply, tobacco smoking cigarettes does therapeutically jeopardize post-operative recovery.
Nasal innervation: Cranial nerve V, the trigeminal nerve (nervus trigeminis) provides sensation to the nose, the face, and the upper jaw (maxilla) - rhinoplasty find this surgery austin. The sensations signed up by the human nose derive from the very first 2 (2) branches of cranial nerve V, the trigeminal nerve. The nerve listings show the respective innervation (sensory circulation) of the trigeminal nerve branches within the nose, the face, and the upper jaw (maxilla).
The shown nerve serves the named structural facial and nasal regions Lacrimal nerve communicates feeling to the skin areas of the lateral orbital (eye socket) region, except for the lacrimal gland. Frontal nerve conveys feeling to the skin areas of the forehead and the scalp. Supraorbital nerve communicates experience to the skin areas of the eyelids, the forehead, and the scalp.

Nasociliary nerve communicates experience to the skin location of the nose, and the mucous membrane of the anterior (front) nasal cavity. Anterior ethmoid nerve conveys feeling in the anterior (front) half of the nasal cavity: (a) the internal original site areas of the ethmoid sinus and the frontal sinus; and (b) the external areas, from the nasal idea to the rhinion: the anterior tip of the terminal end of the nasal-bone suture.
Infratrochlear nerve conveys feeling to the medial region of the eyelids, the palpebral conjunctiva, the nasion (nasolabial junction), and the bony dorsum. Nasal anatomy: The shell-form turbinates (conchae nasales). Nasal anatomy: The septum nasi bones and cartilages. The supply of parasympathetic nerves to the face and the upper jaw (maxilla) originates from the higher shallow petrosal (GSP) branch of cranial nerve VII, the facial nerve.
Not known Details About Austin Rhinoplasty
The floor of the nose makes up the premaxilla bone and the palatine bone, the roofing system of the mouth. The nasal septum is composed of the quadrangular cartilage, the vomer bone (the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone), elements of the premaxilla, and the palatine bones. Each lateral nasal wall includes 3 sets of turbinates (nasal conchae), which are small, thin, shell-form bones: (i) the exceptional concha, (ii) the middle concha, and (iii) the inferior concha, which are the bony framework of the turbinates.