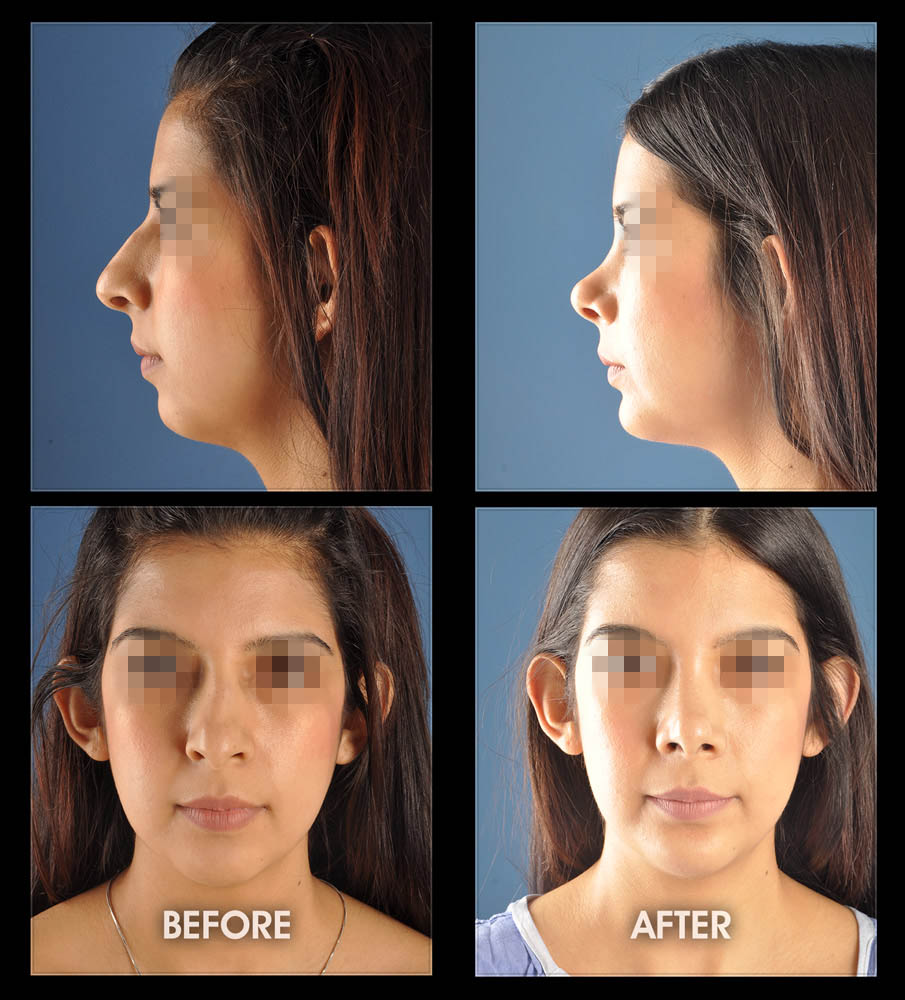
Little Known Facts About Nose Job.
Table of ContentsRhinoplasty Things To Know Before You Get ThisNot known Details About Rhinoplasty Surgery Austin Tx More About Rhinoplasty Surgery Austin
The septum is quadrangular; the upper half is flanked by two (2) triangular-to-trapezoidal cartilages: the upper lateral-cartilages, which are fused to the dorsal septum in the midline, and laterally attached, with loose ligaments, to the bony margin of the pyriform (pear-shaped) aperture, while the inferior ends of the upper lateral-cartilages are totally free (unattached).Below the upper lateral-cartilages lay the lower lateral-cartilages; the paired lower lateral-cartilages swing outwards, from median accessories, to the caudal septum in the midline (the medial crura) to an intermediate crus (shank) area. Finally, the lower lateral-cartilages flare outwards, above and to the side (superolaterally), as the lateral crura; these cartilages are mobile, unlike the upper lateral cartilages.
e., an outward curving of the lower borders of the upper lateral-cartilages, and an inward curving of the cephalic borders of the alar cartilages. The type of the nasal subunitsthe dorsum, the sidewalls, the lobule, the soft triangles, the alae, and the columellaare set up in a different way, according to the race and the ethnic group of the client, therefore the nasal physiognomies denominated as: African, platyrrhine (flat, large nose); Asiatic, subplatyrrhine (low, large nose); Caucasian, leptorrhine (narrow nose); and Hispanic, paraleptorrhine (narrow-sided nose).
The internal nasal valve consists of the location bounded by the upper lateral-cartilage, the septum, the nasal floor, and the anterior head of the inferior turbinate. In the narrow (leptorrhine) nose, this is the narrowest part of the nasal airway. Typically, this area needs an angle greater than 15 degrees for unblocked breathing; for the correction of such narrowness, the width of the nasal valve can be increased with spreader grafts and flaring sutures.
Nasal anatomy: The philtrum. The surgical management of nasal flaws and defects divides the nose into six structural subunits: (i) the dorsum, (ii) the sidewalls (paired), (iii) the hemilobules (paired), (iv) the soft triangles (paired), (v) the alae (paired), and (vi) the columella. Surgical correction and reconstruction understand the entire structural subunit impacted by the defect (injury) or defect, thus, the whole subunit is corrected, specifically when the resection (cutting) of the problem encompasses more than half of the subunit.
The Definitive Guide for Austin Rhinoplasty
The nasofrontal angle, between the frontal bone and the nasion generally is 120 degrees; the nasofrontal angle is more severe in the male face than in the female face. The nasofacial angle, the slope of the nose relative to the aircraft of the face, is around 3040 degrees. The nasolabial angle, the slope between the columella and the philtrum, is approximately 9095 degrees in the male face, and roughly 100105 degrees in the female face.
When observed from listed below (worm's- eye view), the alar base configures an isosceles triangle, with its peak at the infra-tip lobule, right away beneath the suggestion of the nose. The facially proportional projection of the nasal pointer (the distance of the nose's tip from the face) is figured out with the Goode Method, where the projection of the nasal suggestion must be 5560 percent of the distance in between the nasion (nasofrontal junction) and the tip-defining point.
The Goode Method figures out the extension of the nose from the facial surface area by comprehending the distance from the alar groove to the tip of the nose, and then relating that measurement (of nasal-tip projection) to the length of the nasal dorsum. The nasal forecast measurement is acquired by delineating an ideal triangle with lines parting from the nasion (nasofrontal juncture) to the alarfacialgroove. rhinoplasty austin.
55:1 to 0. 60:1, is the ideal nasal-tip-to-nasal-length forecast. Nose Job: Nasal Class I - rhinoplasty austin. The Roman nose. (Nasology Eden Warwick, 1848) Rhinoplasty: Nasal Class II. The Greek nose. (Nasology Eden Warwick, 1848) Rhinoplasty: Nasal Class III. The African nose. (Nasology Eden Warwick, 1848) Nose Job: Nasal Class IV. The Hawk nose. (Nasology Eden Warwick, 1848) Rhinoplasty: Nasal Class V.
( Nasology Eden Warwick, 1848) Nose Job: Nasal Class VI. The celestial nose. (Nasology Eden Warwick, 1848) To determine the client's viability for going through a nose job procedure, the cosmetic surgeon clinically examines him or her with a total medical history (anamnesis) to identify his or her physical and mental health. The prospective client should explain to the physiciansurgeon the practical and aesthetic nasal issues that she or he suffers.

Additionally, additional to physical suitability is mental suitabilitythe patient's mental intention for going through nose surgical treatment is vital to the surgeon's pre-operative evaluation of the patient. The total rhinoplasty surgery austin tx physical assessment of the rhinoplasty client determines if she or he is healthy to go through and tolerate the physiologic tensions of nose surgical treatment.
The 7-Second Trick For Austin Rhinoplasty
Particular facial and nasal evaluations record the patient's skin-type, existing surgical scars, and the balance and asymmetry of the visual nasal subunits. The external and internal nasal evaluation focuses upon the structural thirds of the noseupper section, middle section, lower sectionspecifically noting their structures; the procedures of the nasal angles (at which the external nose jobs from the face); and the physical attributes of the naso-facial bony and soft tissues.
Additionally, when called for, specific teststhe mirror test, vasoconstriction examinations, and the Cottle maneuverare consisted of to the pre-operative evaluation of the prospective rhinoplasty client. Established by Maurice H. Cottle (18981981), the Cottle maneuver is a primary diagnostic method for spotting an internal nasal-valve condition; whilst the patient carefully influences, the surgeon laterally pulls the patient's cheek, consequently simulating the widening of the cross-sectional location of the matching internal nasal valve.